Learning About Microwave Horn Antenna for Everyday Applications
 What is a Microwave Horn Antenna
What is a Microwave Horn Antenna
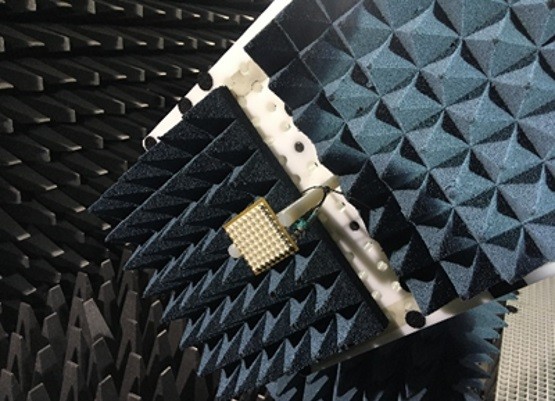
Basic Structure and How It Works
A microwave horn antenna is a type of directional antenna. It uses a flared metal waveguide. This directs radio waves in a specific direction. The basic structure includes a feed waveguide. It also includes a flared opening. This shapes the electromagnetic waves into a beam.
A waveguide is a structure. It guides electromagnetic waves from one point to another. It is commonly used in microwave communications. It is used in radar systems. It is used in other applications. These need high-frequency signals. They need efficient transmission. Waveguides are typically made of conductive materials. They can take various shapes. Such as rectangular or circular tubes.
Horn antennas work by gradually expanding the waveguide’s cross-section. This allows the signal to transition smoothly. It goes from the waveguide into free space. There is minimal reflection. This design enables efficient transmission. It enables efficient reception of microwave signals.
Common Frequencies and Signal Direction
Microwave horn antennas operate across a wide range of frequencies. For example, standard gain horn antennas from RFecho cover frequencies from 0.2 GHz to 40 GHz. They have gains up to 25 dBi. RFecho specializes in the design and manufacture of high-quality standard gain horn antennas, also known as Microwave Horn Antennas.
Horn antennas are highly directional. They radiate energy in a beam-like pattern. This makes them ideal for applications. These require focused signal transmission. Or reception.
Everyday Uses of Microwave Horn Antennas
Microwave horn antennas might hide in plain sight, but they’re the beam-bending pros making modern life zippy, connected, and convenient. From binge sessions to bug-free doors, these horns prove small shapes pack big punches.
Wireless Internet and 5G: Your Streaming Lifeline
Microwave horn antennas play an essential role in modern communication systems. They are used for testing and deploying 5G networks. They are used for satellite uplinks and downlinks. They are used for wireless backhaul connections.
This Broadband Dual-Ridged Horn Antenna is designed for high-performance applications. Including Airborne, Maritime, and Military Radars. 5G communications. Satellite communications. And EMC testing. These antennas support frequency bands. Such as C-band, X-band, Ku-band, and Ka-band. These are critical for advanced satellite communication.
 Satellite TV: Your Evening Binge-Watch Buddy
Satellite TV: Your Evening Binge-Watch Buddy
Craving that next episode? Thank the feed horn in your backyard satellite dish! This little horn sits at the dish’s focal point, grabbing microwave signals from orbiting satellites and funneling them straight to your receiver. It turns weak cosmic pings into crystal-clear HD streams, rain or shine. Without it, your couch potato nights would be a fuzzy flop. Pro tip: Next time you tweak your dish, give that horn a nod—it’s the gatekeeper of your guilty pleasures!
Radar Guns: Keeping the Roads Speedy (and Safe)
Heard that beep from a cop’s radar? That’s a horn antenna in action! Handheld speed guns pack conical or pyramidal horns to shoot microwave beams at your car, bouncing back the echo to calculate your zip. Their narrow beam cuts false reads from pesky trees or semis, nailing your exact speed with laser-like focus. Everyday win: Safer highways, fewer tickets if you ease off the pedal. Horns shine here for short-range radar in traffic cams too—keeping cities flowing smooth.
Behind-the-Scenes Stars: Testing and Everyday Reliability
Horn antennas aren’t flashy, but they’re crucial for calibrating other gadgets—like ensuring your phone’s Wi-Fi antenna performs A+. Labs use them as “gain standards” for precise measurements, keeping your tech trustworthy. In EMI testing, they sniff out interference so your devices play nice. Even in weather radars (hello, accurate forecasts!), horns direct beams for spot-on storm tracking.
In scientific research labs and industrial environments, microwave horn antennas are used for RF testing. EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) compliance tests. Spectrum monitoring. And equipment calibration. Additionally, it also enhances effectiveness in EMC testing.
Their broad frequency coverage allows engineers to test devices across multiple standards efficiently.
Automatic Doors: The Welcoming Wave-Maker
Swing open those mall doors without a touch? Microwave sensors with horn antennas detect your approach, beaming out a focused signal that bounces off you (not the shopping cart behind). It’s like a high-tech “hello” that triggers the whoosh—super reliable in busy spots, ignoring rain or wind. From grocery stores to offices, these horns make entrances effortless and germ-free. Magic? Nah, just smart microwaves!
Microwave Ovens: Dinner in a Dash
Yes, really! The classic kitchen zapper uses a horn-like waveguide to blast microwaves evenly into your leftovers. It’s not a full-blown antenna, but the flared design spreads 2.45 GHz waves for that perfect melt-without-burn. Everyday essential: Hot meals in minutes, no campfire required. (Fun fact: Early horns helped pioneer this tech—talk about a hot invention!)
Radar and Navigation Devices: Where Are You Now
Horn antennas are widely used in radar systems. This is due to their precision. And directional capabilities. They are suitable for airborne radars. Maritime navigation systems. Military surveillance radars. And even automotive radar applications.
Moreover, it is frequently utilized in radar systems. Including airborne, maritime, and military radars. Higher frequencies are essential for precision.
Their ability to support high-frequency ranges. Such as Ku-band or Ka-band. Makes them reliable tools. For detecting objects at long distances. With high accuracy.
Maintenance and Safety Tips
Keeping Your Antenna in Good Condition
To extend your microwave horn antenna’s lifespan:
- Keep it clean from dust or moisture buildup.
- Store it properly when not in use. Preferably inside protective cases.
- Avoid mechanical shocks that could damage internal components.
- Regularly inspect connectors for wear or corrosion.
Following these steps helps maintain performance over time. Without signal degradation.
General Safety Guidelines for Use
When using high-power RF equipment:
- Never stand directly in front of an active transmitting horn.
- Use shielding when necessary during lab testing.
- Make sure all connectors are properly tightened before operation.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines regarding power limits.
Some models can handle up to several kilowatts of power. We offer a wide range of waveguide sizes up to 1kW. So safety precautions must be taken seriously during use.
 FAQ
FAQ
Q: What is the main advantage of using a horn antenna?
A: Horn antennas offer high directionality. With minimal signal loss. Due to their flared waveguide design.
Q: Can I use one horn antenna across multiple frequencies?
A: Yes. Dual-ridged broadband models cover wide ranges. Like 2–32GHz. Broadband dual ridged horn antenna 5.8–20GHz. Making them suitable for various tests.
Q: Are all horn antennas linearly polarized?
A: Not all. While many support linear polarization only. This horn antenna only supports linear polarization. Some models allow dual-polarization measurements. Dual Polarized Horn Antenna. Having a gain from 12 dBi to 17 dBi.

 What is a Microwave Horn Antenna
What is a Microwave Horn Antenna Satellite TV: Your Evening Binge-Watch Buddy
Satellite TV: Your Evening Binge-Watch Buddy FAQ
FAQ