How Log Periodic Dipole Arrays Are Used in Modern Communication Systems

Understanding the Log Periodic Dipole Array Antenna
A log periodic dipole array antenna, or LPDA, is a directional antenna famous for its broad frequency range and reliable radiation pattern. People use it a lot in wireless communication, broadcasting, and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing. This comes from its special design and ability to work with many bands.
The setup of a log periodic antenna has a row of paired metal parts. These parts follow a clear math pattern based on logs. The sizes and gaps between these parts shift by a set ratio. As a result, the antenna keeps good work across a large set of frequencies. This basic but smart plan makes LPDAs easy to use in many places. You can find them inside labs or outside work areas.
Key Features and Design of Log Periodic Dipole Arrays
Log periodic dipole arrays have several main traits. These traits make them fit for work with many bands and wide frequency tasks.
Wideband characteristics
Log periodic antennas can run over a very large frequency span. This helps in communication and RF testing places.
Uniform radiation pattern
They give steady direction and an even signal spread across the work range. This keeps performance strong and steady.
Stable gain
Unlike other type of antennas, LPDAs keep a steady gain level across the frequency range.
For instance, the OLP-270 from RFecho runs from 200 MHz to 7 GHz. It has good gain and solid field strength. Thus, it helps with a sure signal sending and getting in both test and communication spots.
The OLP-00810 log periodic antenna model works from 80 MHz to 1 GHz. It can take up to 3000 watts of continuous wave power. Its VSWR of 1.5:1 (typical) means it sends energy well. At the same time, it cuts down on reflections.
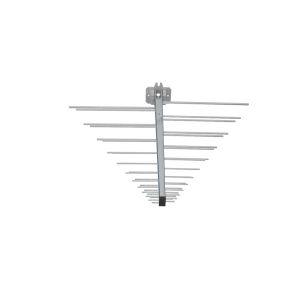
How Log Periodic Dipole Arrays Function in Communication Systems
The way an LPDA works comes from how each dipole part links with different frequencies. When the frequency increases, the part that sends out signals moves to smaller pieces near the feed spot. On the other hand, at lower frequencies, bigger pieces at the back end take over. This way of changing on its own lets the antenna do well over a wide set of waves.
In real use, you do not have to change antennas often. For example, in EMI testing or watching the spectrum, one LPDA can handle all the needed bands. And it does this in just one setup.
A clear case is the OLP213 model. It runs from 200 MHz to 1.3 GHz. This gives wide coverage. Plus, it has a radiation pattern that stays almost the same no matter the frequency. So, it fits well in measurement systems that need both accurate results and easy use.
Advantages of Using Log Periodic Dipole Antennas
Log periodic dipole antennas offer many good points to business and tech users:
- Wide frequency coverage that fits GSM, 4G, 5G, and other wireless setups.
- Consistent performance with steady gain over the whole frequency span.
- Compact and lightweight design, so setup and moving are simple.
- High durability, which works well for outside or moving use.
- Cost efficiency since one LPDA can take the place of several antennas for narrow bands.
A real-world case is the OVLP-00360. This model mixes good gain with a light weight. As a result, putting it in place is not hard. It also has a low antenna factor. This boosts how exact the measures are. At the same time, it lowers signal loss in tough test spots.

Common Applications in Modern Communication Technologies
People use LPDAs in many areas of today’s communication tech:
- Telecommunications: put to use in GSM, 4G, and 5G systems for a steady signal getting.
- Broadcasting: a good pick for TV and radio sending because of its wideband side.
- Radar systems: liked in the army and plane radar for their sharp direction skills.
- Electromagnetic compatibility testing: used in EMC immunity tests due to their strong power hold.
- Aerospace communication: picked for satellite and UAV systems that need coverage for many bands.
One handy example is the OLP-00270. It works well from 25 MHz to 7000 MHz. And it keeps trust in both inside and outside spots. Workers often pick it for mixed RF places. These include GSM, WiFi, and 5G signals.
Comparison with Other Types of Communication Antennas
How do log periodic dipole arrays stack up against other antennas? Think of horn or omnidirectional types.
Horn antennas, like the ODPA-0620-15, can manage continuous power up to 500 W. They also give cross-polarization isolation above 30 dB. These shine in exact radar and lab work. However, their frequency range is small.
Omnidirectional antennas, such as the OBC-1060-20W-1, cover 1000 MHz to 6000 MHz. But they send signals in every direction. This makes them right for basic signal spread. Still, they miss the focused power that LPDAs have.
In contrast, log periodic dipole array antennas bring both direction and wideband work. They keep a steady gain and easy change. For this reason, they are a smart pick for workers who want large frequency cover without losing grip.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Log Periodic Dipole Array
Before you pick an LPDA for your work, think about these points:
- Frequency range: Make sure the model covers all the bands you need. The OLP-270 takes care of 200 MHz to 7 GHz. This gives a wide reach.
- Gain requirements: more gain means stronger signals. But it makes the beam narrower.
- VSWR: pick a low VSWR like 1.5:1 or <2:1. This cuts back on power that bounces back.
- Power handling: for systems with high power, go for antennas like the OLP-00810. It holds 3000 W continuous wave.
- Installation environment: for outside or moving setups, you need a strong build.
Some models, like the OVLP-O0830, let you shift polarization from E-plane to H-plane with ease. This kind of change helps in system tests. It also aids in tweaks for top results.
FAQ
Q1: What makes a log periodic dipole array different from a regular dipole?
A standard dipole works at one fixed frequency. In contrast, a log periodic dipole array can manage many frequencies. This is thanks to how its parts are set up.
Q2: Can one LPDA be used for both transmitting and receiving?
Yes. Many models, such as the OLP-00360, are made for work in both directions. This makes them good for tests that go both ways.
Q3: What is a good option for long-range LPDA use?
The OVLP-O0830 is a top choice. It has over 8 dBi gain across 80 MHz to 3 GHz. So, it gives far reach and sure work.
Conclusion
Log periodic dipole array antennas mix direction, steadiness, and wideband skill in one small shape. They act as a smart fix for fields like telecom, EMC testing, and aerospace communication.
When you pick an LPDA, pay attention to frequency range, gain, VSWR, and power handling. Match these to what your project needs. RFecho offers many LPDA models for pro use. Each one is checked for steady work and long life.
For more info or tech details, reach out to RFecho’s sales team. They can talk about the best LPDA for your next system join.