How a Puck Antenna Functions
Consider a gadget that is compact enough to fit in your hand, yet powerful enough to connect drones, tractors and cars to the global satellite network. Say hello to the puck antenna, hockey-puck-shaped antenna capable of transforming navigation and communication across sectors. It’s more than a basic tool. This discreet antenna provides omnidirectional signal transmission and reception. It ensures smooth GPS tracking and data transfer in tough conditions. It guides autonomous farm equipment across vast fields. It keeps drones on track in urban canyons. Puck antennas are the hidden champions of modern connectivity. Their sturdy, low-profile design suits fleet management to marine navigation. In this article, we’ll explore how these versatile antennas function and examine their innovative applications. We’ll reveal what makes them unique in the realm of advanced communication solutions.
 What Is a Puck Antenna?
What Is a Puck Antenna?
Explaining the Puck Antenna Design
A puck antenna is a small, covert antenna that typically resembles the shape of a hockey puck. That’s where its origin lies. It’s used for omnidirectional reception and transmission of signals, which means it can receive and transmit signals in every direction horizontally. It’s shaped in a manner that it can be placed on flat surfaces like the roof of cars, drones, or equipment cases without any visibility. Because of its minimal size and streamlined design, it’s perfect for mobile applications where space and drag are an issue.
General Applications Across Sectors
Puck antennas are tremendously versatile and hence widely used in different areas because of their dependable performance. Within the transport industry, they are used on fleet vehicles for GPS tracking purposes and are constantly. In agriculture, they are mounted on autonomous equipment to guide them accurately. UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles) use them for telemetry and location pinpointing through GPS. Apart from that, they are employed in marine navigation devices, land surveying equipment, and industrial IoT configurations.
These benefits make the antenna a prime candidate for electronic warfare, direction-finding, telemetry, and surveillance applications, and airborne flush-mount use.
 Differences of Puck Antennas VS Other Antenna Types
Differences of Puck Antennas VS Other Antenna Types
The horn or Yagi antennas are directional with high gain and transferring energy in specific direction, while puck antennas are wider with lower gain. This suits them well for everyday communication or tracking needs where a steady connection matters more than direction. Meanwhile, specialized types like dual-polarized horn antennas focus on high-frequency tasks with tight beams for testing or radar. In contrast, puck antennas emphasize simplicity, toughness, and hassle-free setup.
How a Puck Antenna Works
Signal Reception and Transmission Principles
A puck antenna functions by harnessing electromagnetic wave propagation. It grabs radio frequency (RF) signals from satellites or base stations through its internal components. These signals then travel via coaxial cables to the receiver unit. On the flip side, when sending data in systems like two-way communication, the antenna emits RF signals outward from its central point.
Its omnidirectional pattern keeps signal strength fairly even across the horizontal plane around it.
Internal Components and Their Roles
Inside a typical puck antenna, you’ll find one or more radiating elements, often patch or helical designs, housed in a weather-resistant shell. Many versions also come with a built-in low-noise amplifier (LNA). This component strengthens faint incoming signals before they reach the receiver.
An antenna with active components paired with a low-noise amplifier is known as an active antenna. A micro-strip antenna and low noise amplifier (AILNA) are crafted and combined on a single substrate. This creates high gain and a smaller device, ideal for GPS receiver applications.
Frequency Ranges and Supported Bands
Puck antennas cater to different frequency bands based on their purpose. More advanced models might support BDS (BeiDou) frequencies like B1/B2/B3 or Galileo’s E5/E6 bands. This boosts precision in global navigation satellite system (GNSS) tasks.
 Exploring the Usage of Puck Antennas in Navigation
Exploring the Usage of Puck Antennas in Navigation
Overview of GPS Functionality in Puck Antennas
GPS puck antennas are carefully designed to capture satellite positioning signals with accuracy, even in tough spots like urban canyons or thick forests. Their build focuses on clear signals through features like right-hand circular polarization (RHCP) and wide beam width reception. Some also have filtering circuits to cut down on interference.
Key Features of a Dual GPS Puck
A dual GPS puck is an antenna that can pick up multiple GNSS signals at once across various frequencies, like L1/L2 from GPS or B1/B3 from BeiDou, all in one small unit.
The OGGG-BD-36-P is a four-system, multi-frequency aviation antenna that supports GPS, BDS, GLONASS, and GALILEO. Its broad frequency bandwidth allows for multi-system and multi-frequency operations.
This dual feature improves location accuracy by enabling differential corrections across bands. It also strengthens signal reliability against multipath errors.
Additionally, this passive antenna delivers high gain and a wide beam width. It excels at receiving low elevation signals, ensuring steady star collection even in areas with heavy signal blockage.
Use Cases for GPS Puck Antennas in Navigation and Tracking
GPS puck antennas play key roles in navigation across different sectors:
- UAVs: Support precise flight control for mapping tasks.
- Agriculture: Guide autonomous tractors along rows.
- Fleet Management: Track trucks in real time for location updates.
- Surveying:Ensure stable GNSS reception on portable mapping devices.
They’re essential in many situations, greatly boosting farming efficiency. In aerial photography, they’re perfect for mapping and GIS applications.
Installation and Performance Considerations
Mounting Options and Environmental Durability
Puck antennas can be secured with magnetic bases or adhesive pads, depending on the surface. Durable models often carry IP65/IP67 ratings, offering protection from dust and water exposure.
Compact and light, the antenna reaches an IP67 protection level once assembled. This gives it solid resistance to water and physical impact.
Such features make them a great fit for outdoor use, including on vehicles in rainy conditions or in marine settings.
Factors Affecting Signal Quality and Accuracy
A few elements can impact performance:
- Obstructions:Trees or buildings might block satellite views.
- Interference:Nearby devices could create disruptive RF noise.
- Antenna Placement: Positioning near metal surfaces may warp radiation patterns.
High out-of-band rejection helps tackle these issues:
Moreover, strong out-of-band rejection reduces interference from outside sources like communication base stations.
For best results, place puck antennas where they have a clear view of the sky, away from large metallic objects.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Term Efficiency
To keep them working well:
- Check connectors regularly for signs of rust.
- Wipe debris off the outer casing.
- Make sure waterproof seals stay secure.
- Swap out damaged cables without delay.
- Run signal quality checks often using GNSS receivers.
These steps help prolong their lifespan, especially in rough outdoor environments.
FAQ
Q1: What is the difference between an active and a passive puck antenna?
A:An active antenna has a built-in low-noise amplifier (LNA) to improve weak signal reception. Passive ones depend entirely on their structure without any boost.
Q2: Can one puck antenna support multiple GNSS systems?
A:Yes. The OGGG-BD-33-M is a four-system, multi-frequency handheld antenna compatible with GPS, BDS, GLONASS, and GALILEO, ideal for worldwide coverage.
Q3: Are dual GPS pucks better than single-band ones?
A:Dual-band versions offer better precision through correction methods between L1/L2 frequencies. They also resist interference and obstacles more effectively.
Q4: How should I install my GPS puck antenna?
A:Set it flat on a surface with little blockage overhead. Choose a mounting option that fits your setup, like a magnetic base for cars or an adhesive pad for fixed spots.
Q5: Do I need waterproofing features?
A:Definitely, if it’s used outside. Opt for models with at least IP65/IP67 ratings, which greatly enhance reliability for devices like UAVs in wet conditions.
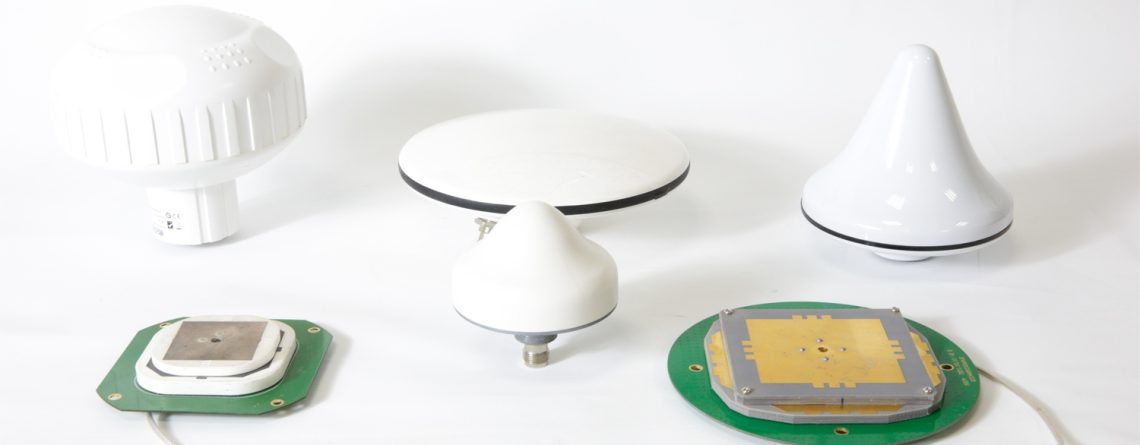
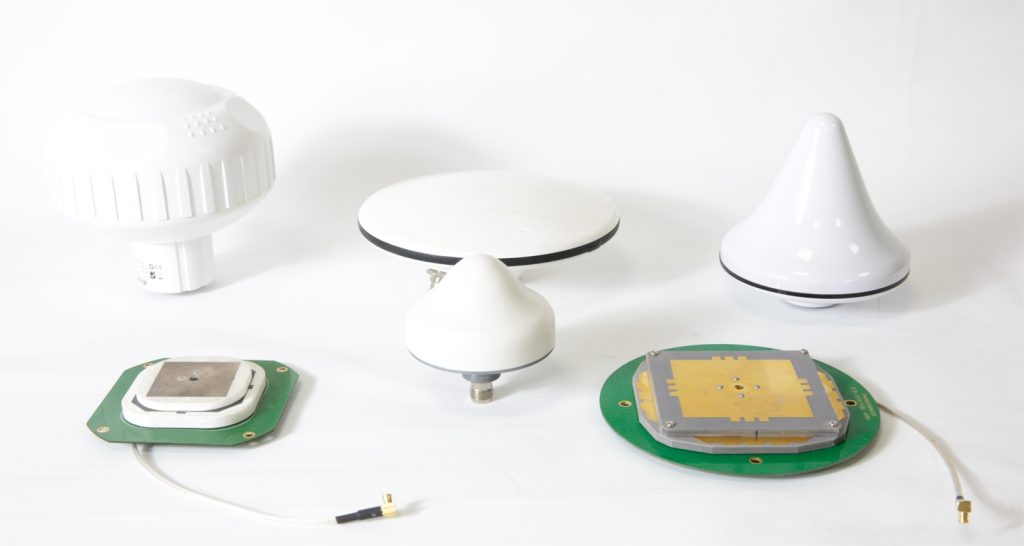

 What Is a Puck Antenna?
What Is a Puck Antenna? Differences of Puck Antennas VS Other Antenna Types
Differences of Puck Antennas VS Other Antenna Types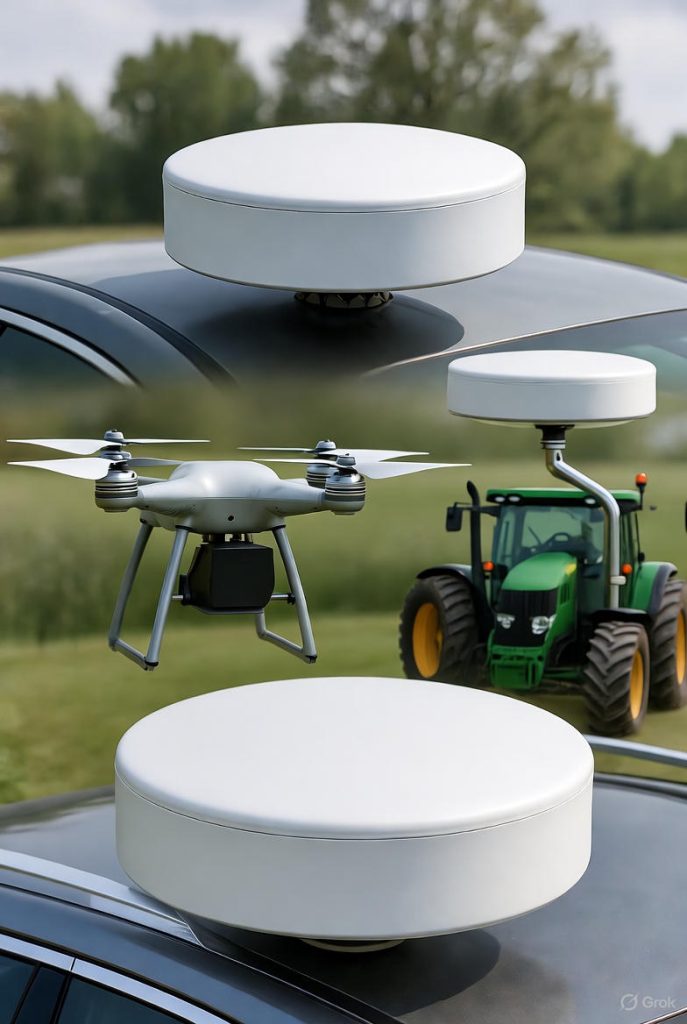 Exploring the Usage of Puck Antennas in Navigation
Exploring the Usage of Puck Antennas in Navigation