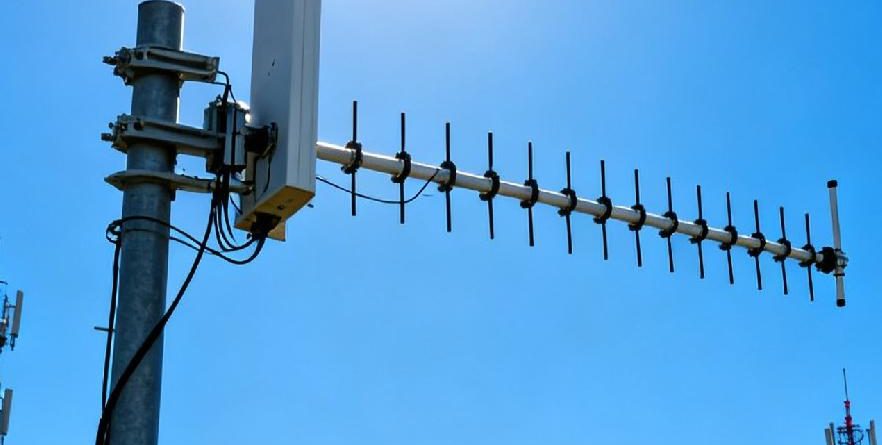
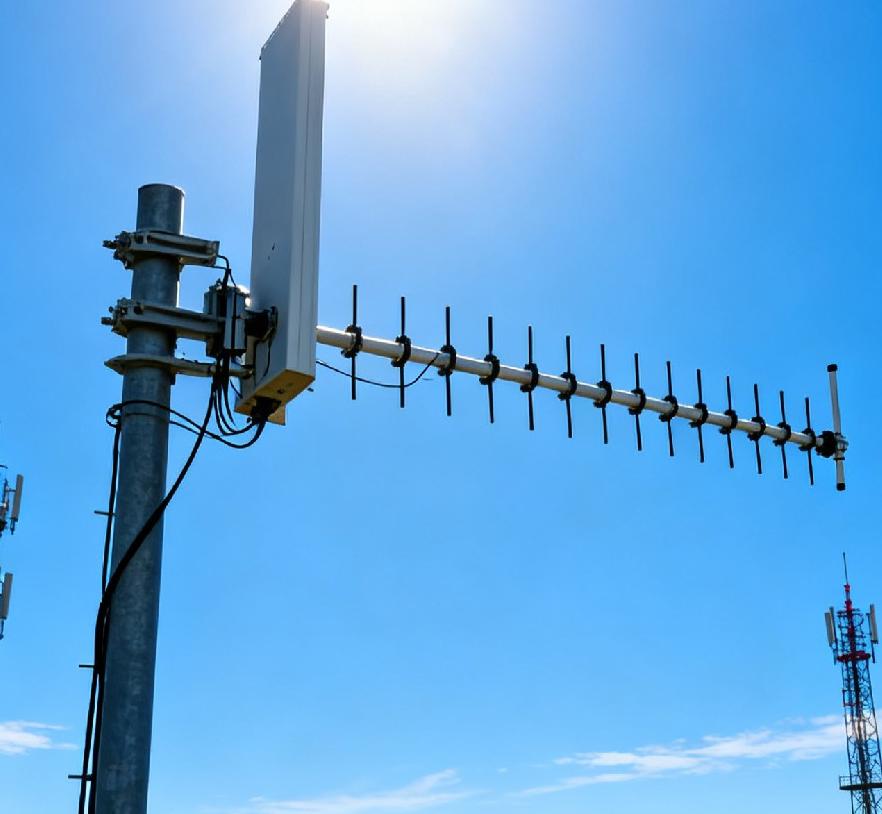
What Is a Log Periodic Antenna Array

Introduction
Antennas hold a vital place in today’s wireless communication setups. They act as the link between radio waves moving through the air and electrical signals flowing through wires or circuits. Among various antenna types, the log periodic antenna array (LPAA) shines because of its special build and wide-range working capabilities.
A Log Periodic Antenna Array is a kind of directional antenna. It works over a broad set of frequencies. Its main trait is the log-periodic design. This setup helps it keep steady performance in different bands.
Key features of a log-periodic antenna include: Wideband characteristics: Log-periodic antennas can function over a broad frequency span. This makes them fit for many communication and RF tasks. These antennas also provide good directivity. As a result, they focus energy in certain directions. This boosts signal power.
Understanding the Design of a Log Periodic Antenna Array
Basic Structure of an LPAA
The core of every LPAA features a row of dipole elements. Each one has a unique length and gap. These dipoles sit on a boom. They follow a precise geometric pattern based on logarithmic scaling.
The build of a log-periodic antenna has paired metal parts set in a logarithmic periodic way. The lengths and spaces of these parts grow or shrink following the logarithmic periodic rule. This setup lets the antenna manage several frequency bands with one physical form.
Operating Principle
The LPAA works on the idea that only some dipoles vibrate at a specific frequency. Different lengths mean certain elements turn active based on the frequency of sending or receiving.
The way a log-periodic antenna runs comes from the varied lengths and spaces of elements in each frequency zone. This lets the antenna fit the radiation needs at different frequencies. So, it shows steady radiation traits as frequency changes. That quality makes it great for wideband uses.
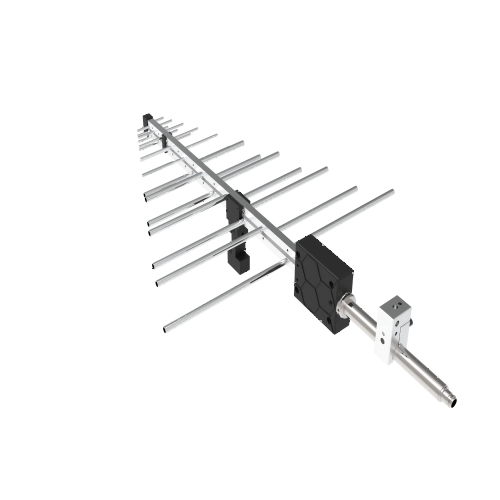
Key Features of Log Periodic Antenna Arrays
Frequency Range
One major plus of LPAA is its wide frequency reach. Common models handle from 80 MHz up to a few GHz. For instance, the OLP-270 is a flexible, strong-performing log-periodic antenna for many tasks. It has fine broadband traits and covers a large frequency span from 200 MHz to 7GHz.
This quality makes them very apt as UHF log periodic antennas for TV broadcasting or RF testing.
Directivity and Gain
LPAAs are directional antennas. They direct energy in one way. This trait boosts signal power and cuts noise from other spots.
By piling up several log-periodic elements, the antenna gets better gain and directivity. Thus, it improves signal receiving and transmitting characteristics. Gain levels often ranges from 6dBi to more than 8dBi. Some models reach even higher.
Impedance Characteristics
Impedance matching matters a lot for good power flow between the antenna and linked devices. Most LPAAs offer 50Ω impedance. They also have low VSWR (<2:1). This cuts signal bounce.
The OLP-00810 shows a VSWR of 1.5:1 (typ.) and 50Ω impedance. It ensures smooth sending across its work range.
Polarization
LPAA antennas usually back linear polarization. This antenna’s build gives perks like simple starting, good gain, directivity work, and high peak power handling. It supports linear polarized waves. This polarization matches many common signals in communication setups.

Applications of Log Periodic Antenna Arrays
Wideband Communication Systems
Because of their ability to cover a wide frequency area, LPAA antennas see heavy use in broadband communication systems like satellite links, RF monitoring, and field test arrangements.
The OLP213 comes with single calibrations per ANSIC63.5, CISPR16-1-6, and SAEARP958. It includes a bracket for simple setup on tripods. It’s perfect for transmitting and receiving over broad spans such as 200 MHz to 1.3 GHz.
Radar Systems
Radar setups gain from LPAA’s broadband and directional. Plus, this antenna fills a key role in radar systems. It serves in advanced tasks like car radar and watch systems.
The power to check many frequencies allows exact target spotting and sizing.
EMC and RF Testing
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing needs antennas that span many bands well. LPAA builds jobs perfectly. They offer steady gain and low VSWR.
The OBH-230 Broadband dual ridged horn antenna works well for EMC testing systems and telecommunications tasks. It shines especially from 0.4GHz to 6GHz.
Television and Radio Broadcasting
Many over-the-air TV signals run in the VHF and UHF bands. It fits well for TV broadcasting. There, over-the-air TV signals work in lower frequency bands. It also suits other broadcast services. LPAA antennas’ characteristics makes them key in broadcast towers and home setups.
Advantages of Log Periodic Antenna Arrays
Broadband Performance
A main benefit is the LPAA’s is to operate over wide frequencies without tweaks or tuning. Log-periodic antennas can run over a broad frequency range. This makes them suitable for various communication and RF applications.
This removes the need to change antennas during tests or setups. It saves time and money.
Directional Sensitivity
Their directional characteristics lets users point the antenna at exact sources. This raises pickup quality. At the same time, it blocks noise from other paths. The stacked elements boost the total gain and directivity of the antenna. This strengthens signals and directs radiation in set ways.
This setup makes them perfect for point-to-point tasks or signal-split tasks.
High Gain and Efficiency
The LPAA build makes sure the gain stays strong across all backed frequencies. For example, the OLP-270 gives high gain. It lets users reach higher field strengths easily. This ensures top signal transmitting and receiving characteristics.
High gain with low VSWR means good power use. It’s key in both test labs and field jobs.
Conclusion
Log periodic antenna arrays mix simple engineering with strong performance traits. These include wideband operation, high gain, steady impedance matching, and firm directivity. Log-periodic antennas see wide use in broadcasting, wireless communications, radar systems, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and aerospace fields. Whether you face RF testing spots or real-world communication setups like TV broadcasting or public safety networks, LPAA antennas bring top flexibility. With models like the OLP-270 or OVLP-00360 out now, engineers get strong tools. These ease the broadband signal work. At the same time, they max out efficiency.
Ready to enhance your broadband testing or communication setup? Explore RFecho’s full range of log-periodic antennas and find the model that fits your frequency, gain, and application needs. Contact our team today for technical support or a customized solution.
FAQ
Q1: What is a log periodic antenna array best used for?
A log periodic antenna array suits wideband applications. These include RF testing, broadcasting, radar systems, and wireless communication.
Q2: How does an LPAA differ from other directional antennas?
Unlike narrowband directional antennas like Yagi-Uda, LPAAs back multiple frequency bands at once. This comes from their special element setup.
Q3: Can I use an LPAA indoors?
Yes. Many small LPAAs, like the OLP-00810, are made for mobile or indoor use. They help in RF measurements or watching tasks.
Q4: What type of polarization do LPAAs use?
Most LPAA models use linear polarization. It lines up well with many modern wireless systems. These include LTE and Wi-Fi.
Q5: Are LPAAs suitable for EMC compliance testing?
Yes. Their wide frequency reach and tuned performance make them great tools for EMC compliance testing. They work on emissions and immunity checks.